Controlling GPIO pins More...
Functions | |
| void | gpio_toggle (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t gpios) |
| Toggle a Group of Pins. More... | |
| static uint8_t | gpio_read (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t gpios) |
| Get status of a Group of Pins (atomic) More... | |
| static void | gpio_write (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t gpios, uint8_t data) |
| Set level of a Group of Pins (atomic) More... | |
| static void | gpio_set (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t gpios) |
| Set a Group of Pins (atomic) More... | |
| static void | gpio_clear (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t gpios) |
| Clear a Group of Pins (atomic) More... | |
| static uint8_t | gpio_port_read (uint32_t gpioport) |
| Read level of all pins from a port (atomic) More... | |
| static void | gpio_port_write (uint32_t gpioport, uint8_t data) |
| Set level of of all pins from a port (atomic) More... | |
Detailed Description
Controlling GPIO pins
Each I/O port has 8 individually configurable bits. When reading and writing data to the GPIO ports, address bits [9:2] mask the pins to be read or written. This mechanism makes all GPIO port reads and writes on the LM4F atomic operations. The GPIO API takes full advantage of this fact to preserve the atomicity of these operations.
Setting or clearing a group of bits can be accomplished with gpio_set() and gpio_clear() respectively. These operation use the masking mechanism described above to only affect the specified pins.
Sometimes it is more appropriate to read or set the level of a group of pins on a port, in one atomic operation. Reading the status can be accomplished with gpio_read(). The result is equivalent to reading all the pins, then masking only the desired pins; however, the masking is done in hardware, and does not require an extra hardware operation.
Writing a group of pins can be accomplished with gpio_write(). The mask ('gpios' parameter) is applied in hardware, and the masked pins are not affected, regardless of the value of the respective bits written to the GPIO port.
Two extra functions are provided, gpio_port_read() and gpio_port_write(). They are functionally identical to gpio_read (port, GPIO_ALL) and gpio_write (port, GPIO_ALL, val) respectively. Hence, they are also atomic.
GPIO pins may be toggled with gpio_toggle(). This function does not translate to an atomic operation.
- Note
- The gpio_toggle() operation is the only GPIO port operation which is not atomic. It involves a read-modify-write cycle.
Suppose PA0, PA1, PA2, and PA3 are to be modified without affecting the other pins on port A. This is common when controlling, for example, a 4-bit bus:
Suppose a LED is connected to PD4, and we want to flash the LED for a brief period of time:
Function Documentation
◆ gpio_clear()
|
inlinestatic |
Clear a Group of Pins (atomic)
Clear one or more pins of the given GPIO port. This is an atomic operation.
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios GPIO pin identifiers. Any combination of pins may be specified by OR'ing then together.
Definition at line 298 of file gpio.h.
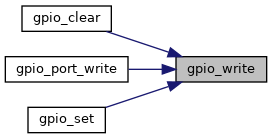
References gpio_write().

◆ gpio_port_read()
|
inlinestatic |
Read level of all pins from a port (atomic)
Read the current value of the given GPIO port. This is an atomic operation.
This is functionally identical to gpio_read (gpioport, GPIO_ALL).
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses
- Returns
- The level of all the pins on the GPIO port.
Definition at line 314 of file gpio.h.
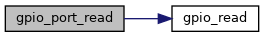
References GPIO_ALL, and gpio_read().
◆ gpio_port_write()
|
inlinestatic |
Set level of of all pins from a port (atomic)
Set the level of all pins on the given GPIO port. This is an atomic operation.
This is functionally identical to gpio_write (gpioport, GPIO_ALL, data).
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios GPIO pin identifiers. Any combination of pins may be specified by OR'ing then together. [in] data Level to set pin to. Bit 0 of data corresponds to GPIO0, bit 1 to GPIO1. and so on.
Definition at line 333 of file gpio.h.
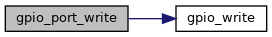
References GPIO_ALL, and gpio_write().
◆ gpio_read()
|
inlinestatic |
Get status of a Group of Pins (atomic)
Reads the level of the given pins. Bit 0 of the returned data corresponds to GPIO0 level, bit 1 to GPIO1 level. and so on. Bits corresponding to masked pins (corresponding bit of gpios parameter set to zero) are returned as 0.
This is an atomic operation.
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios GPIO pin identifiers. Any combination of pins may be specified by OR'ing then together.
- Returns
- The level of the GPIO port. The pins not specified in gpios are masked to zero.
Definition at line 249 of file gpio.h.
References GPIO_DATA.
Referenced by gpio_port_read().
◆ gpio_set()
|
inlinestatic |
Set a Group of Pins (atomic)
Set one or more pins of the given GPIO port. This is an atomic operation.
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios GPIO pin identifiers. Any combination of pins may be specified by OR'ing then together.
Definition at line 284 of file gpio.h.
References gpio_write().
◆ gpio_toggle()
| void gpio_toggle | ( | uint32_t | gpioport, |
| uint8_t | gpios | ||
| ) |
Toggle a Group of Pins.
Toggle one or more pins of the given GPIO port.
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios Pin identifiers. GPIO pin identifiers
◆ gpio_write()
|
inlinestatic |
Set level of a Group of Pins (atomic)
Sets the level of the given pins. Bit 0 of the data parameter corresponds to GPIO0, bit 1 to GPIO1. and so on. Maskedpins (corresponding bit of gpios parameter set to zero) are returned not affected.
This is an atomic operation.
- Parameters
-
[in] gpioport GPIO block register address base GPIO register base addresses [in] gpios GPIO pin identifiers. Any combination of pins may be specified by OR'ing then together. [in] data Level to set pin to. Bit 0 of data corresponds to GPIO0, bit 1 to GPIO1. and so on.
Definition at line 269 of file gpio.h.
References GPIO_DATA.
Referenced by gpio_clear(), gpio_port_write(), and gpio_set().